- 2025-07-22
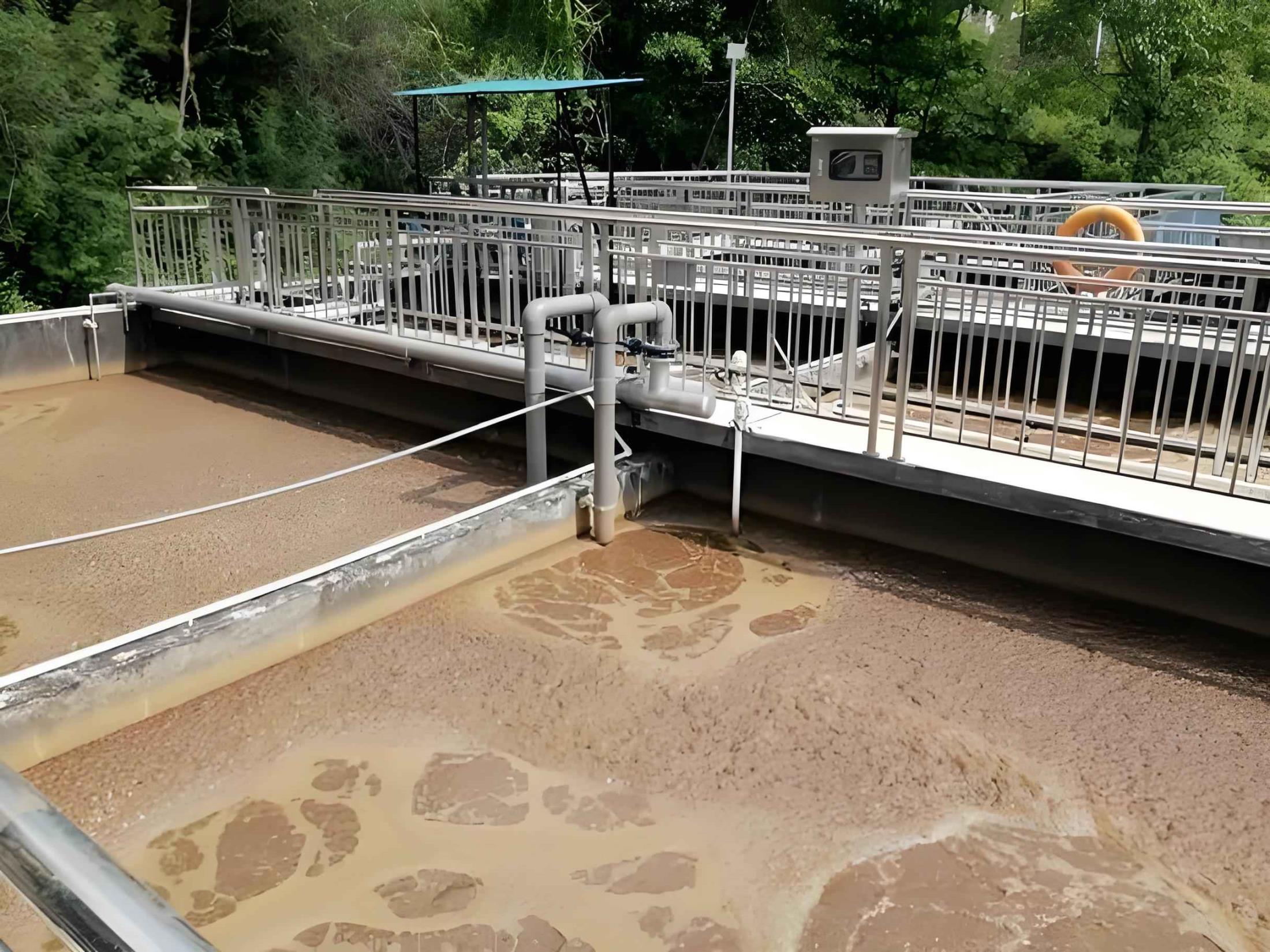
Leachate treatment
Leachate characteristics and treatment difficulties
Formation mechanism:
Rainwater infiltration (accounting for ≥70%) and waste biochemical reaction liquid
Typical pollutant concentrations:
COD: 5,000-60,000 mg/L
NH₃-N: 500-3,000 mg/L
Heavy metals: Zn/Cr/Pb total 10-50 mg/L
Environmental risks:
1 mg of leachate can pollute 1 m³ of groundwater (according to the Class III limit of the Groundwater Quality Standard)
Core treatment process combination
1. Pretreatment system
Media filter: remove ≥50μm suspended solids (filtration rate 8-10m/h)
Ultrafiltration (UF) unit:
Molecular weight cutoff: 100 kDa
Flux maintenance: 15-25 LMH (transmembrane pressure difference ≤0.3MPa)
2. Deep treatment link
"MBR+RO" double membrane process:
MBR sludge concentration: 12-18g/L (SRT>50 days)
RO desalination rate: >98% (rolled polyamide membrane, pressure 4.0-6.0MPa)
Evaporation crystallization backup:
Applicable to RO concentrated water (TDS>50,000mg/L), steam consumption 0.8-1.2t/t water
3. Deep removal guarantee
Ozone catalytic oxidation:
O₃ dosage 80-120mg/L, CT value>15 mg·min/L
Activated carbon adsorption:
Iodine value ≥900mg/g, carbon bed space velocity 2-4 BV/h
Project case of a provincial capital landfill
Processing scale: 800 tons/day
Raw water quality:
COD=38,500mg/L, NH₃-N=2,150mg/L
Process flow:
Regulating tank→anaerobic UASB→MBR→RO→ozone activated carbon
Operation effect:
COD reduced to <100mg/L (removal rate 99.7%)
NH₃-N reduced to <8mg/L
Cost of water treatment per ton: ¥35-42 (including depreciation)