- 2025-07-28
What is a Media Filter and How to Choose One? | Media Filter Guide 2025
1. Introduction
Did you know that particles like sand, silt, leaves, and other impurities can interfere with water filtration processes such as reverse osmosis? This is where media filters come in handy! Whether it’s irrigation water, industrial cooling water, or water contamination in a small aquarium or large swimming pool, media filters effectively remove suspended solids. The material of these filters depends on factors such as filtration needs, location of use, particle size, and filtration efficiency.
Are you curious about how media filters work and how to choose the right one? Don’t worry! This guide will explain the principles, types, applications, and importance of media filters in commercial and industrial settings.
2. What is a Media Filter?
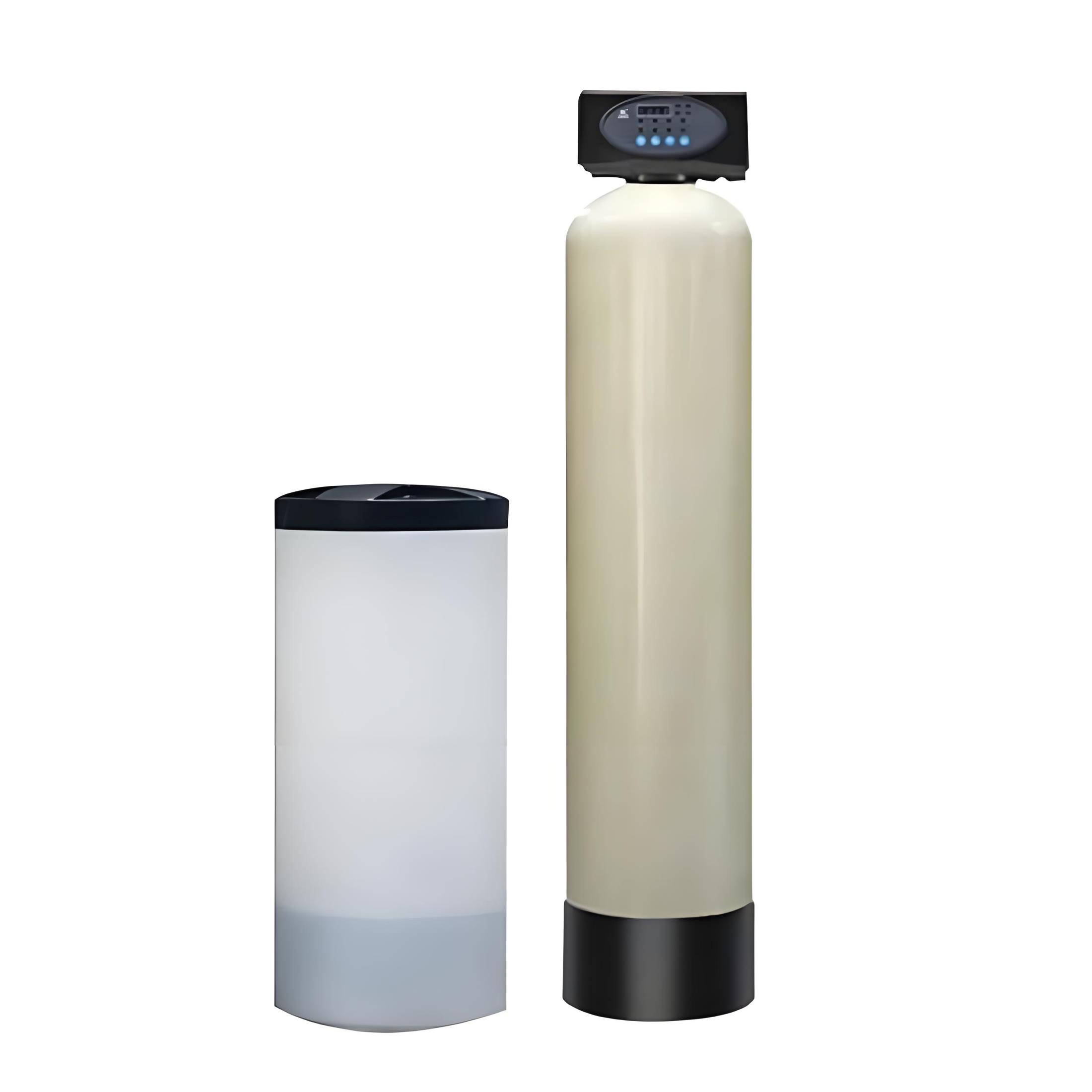
A media filter is a type of water filtration device that is primarily used to capture and remove all suspended solids such as fine particles, clay, grit, organic matter, and algae from raw water. Media filters can be made of one or more layers. Generally speaking, a multi-media filter consists of four main layers: coal, sand, garnet, and a gravel support layer at the bottom. Media filters are widely used in many industries such as oil and gas, chemicals, power generation, municipal water treatment, and construction engineering.
The role of media filters in water treatment
You may wonder why we need media filters when we already have advanced filtration technology such as reverse osmosis membrane filtration? The reason is that larger impurities and suspended solids will reduce the water pressure required for effective reverse osmosis production and clog the membrane pores of the reverse osmosis membrane. This situation will not only lead to membrane fouling, but also increase maintenance costs.
3. How media filters work / media filtration water treatment process
The filtration process of media filters is to let water flow through three main layers: coal, sand, and garnet, and the last layer of gravel that serves as a support (non-filtering) layer. All of these layers will capture particulate matter or suspended solids, and the filtered water will pass through these layers.
The top layer of coal evenly distributes the water throughout the media, while the sand and garnet layers effectively remove particulate matter. The porous structure of the first three layers of media effectively reduces contaminants in the water without affecting efficient water flow. By removing all suspended solids, the media ensures that the water quality meets water standards.
The final layer of gravel is mainly to physically support the top three layers of filter media. It provides support to ensure even water flow and prevents channeling.
4. What does this device remove?
Multimedia filters can reduce the SDI (Slit Density Index) and TSS (Total Dissolved Solids) in the incoming water. In simple terms, it reduces suspended solids and makes the water clean and fresh for subsequent use.
An effective media filter is said to remove particles as small as 15-20 microns. It can remove all large-sized particles, such as leaves and rocks, and even small-sized particles, such as cracks, clay, garnet, algae, and even some microorganisms, depending on the layering method used by the multimedia filter.
5. What are the filter media?
Media filters can consist of one, two or more layers. Depending on the level of water contamination and the required filtration efficiency, you can choose from the following types:
Single Media Filter: This is the simplest type of media filter, with only one layer of sand or coal.
Dual Media Filter: This type of filter contains two layers, usually sand and coal.
Multimedia Filter: This filter can have more than two layers. The media can be coal, sand, garnet and gravel.
In a multi-media filter, there is an additional layer of garnet between the upper and bottom gravel layers. This layer of garnet prevents fine particles from entering the gravel layer and then flowing out of the filter. In addition, the gravel layer supports all the upper layers and prevents the formation of channels. Usually, the pore size of each layer decreases from top to bottom.
6. How to choose a multimedia filter?
When choosing a multimedia filter, there are various factors to consider, and each factor plays a vital role in the quality of our filtered water. Let's take a look at how to choose a multimedia filter:
Understand the water quality: The first thing to consider is the water quality of the site. Identify the contaminants and make sure to choose the right type of multimedia filter. If the contaminants are large, just use the anthracite and gravel layers; if the contaminants are small, you will also need to use garnet and sand layers.
Filter media type: Multimedia filters can be divided into three types according to the number of media layers: single media, dual media and multimedia filters. Common media types are sand, gravel, anthracite and garnet. The top layer of anthracite can filter out larger particles in the raw water, such as leaves or rocks. Meanwhile, sand and garnet are used to filter out smaller particles, such as algae and microorganisms.
Micron rating: Multimedia filters can generally remove contaminants as small as 20 microns in the water, while filters with added coagulants can filter contaminants 10 microns or even smaller. Before purchasing a multimedia filter, be sure to check its micron rating to ensure the filtration effect.
Backwash: Make sure the multimedia filter you purchase has an effective backwashing program, as it helps to rejuvenate the filter media and remove contaminants. Backwashing is to let the water flow in the opposite direction, sometimes with the help of air flushing, to remove contaminants trapped in the filter. The air can expand the filter membrane, and the water can flush away the trapped contaminants.
7. Advantages of multimedia filters
Multimedia filters have many advantages in water treatment plants. They have diverse filtering functions and are easy to use. Here are some of them:
Environmental protection: Multimedia filters can effectively remove various harmful impurities in water, while protecting water resources, it also helps to reduce the negative impact on the environment.
Effective removal of pollutants: The design purpose of the media filter is to remove particles (usually large particles) and small particles in the water. Through the layered filtration method, each layer contains gravel, garnet and sand, which can effectively remove particles of different sizes.
Extend the life of the membrane system: As a pretreatment system for the membrane treatment system, this system can effectively filter out large particles and suspended solid particles, reduce the wear of membrane accessories, and extend their service life.
Customizability: Multimedia filters can be customized based on the number of layers. This flexibility allows us to use versatile and customized filtration systems that can accommodate different filtration requirements, depending on water quality standards.
Longer operation: Multimedia filters can operate for longer periods of time without frequent maintenance. Because it is composed of multiple layers, each layer takes time to reach its limit of contaminant capture.
Improved water quality: Multimedia filters can improve water purity and remove odors, colors, and particles from raw water, thereby improving the quality of water received by the end user.
Wide applicability: It is suitable for reverse osmosis system pretreatment, industrial wastewater treatment, agricultural irrigation, food and beverage processing plants, swimming pools, municipal water supply systems and other fields.
Low maintenance cost: Multimedia filters generally require low maintenance costs and are relatively simple, thereby reducing operating costs.
8. Media Filters vs. Conventional Filters
Compared to conventional or traditional filters, media filters can contain multiple layers (multi-layer filters) and capture a variety of particles in each layer. Therefore, since multimedia filters will reach the limit of their contaminant capture capacity after a longer period of operation, they require less maintenance.
Multimedia filters are considered more flexible and efficient at removing particles than regular filters. Media filters can also be customized (with different numbers of layers) to target specific contaminants.
Another difference is the size of the contaminants that the filter is able to remove. Regular filters have a filtration accuracy of 50 microns, while media filters can remove particles as small as 10-15 microns.
9. Types of Multimedia Filters and Their Applications
There are many types of multimedia filters, each with its own specific layering method, contaminant removal capabilities, micron ratings, and application scenarios. Here are the types of multimedia filters and their applications:
Sand Media Filter: Uses sand as the main filter medium and is suitable for removing larger particles of impurities, such as sand, soil, and suspended solids.
Carbon Media Filter: Uses activated carbon as the filter medium and is effective in removing organic matter, chlorine, and odors in drinking water and water treatment applications.
Ceramic Media Filter: Made of ceramic materials, it is suitable for a variety of commercial or industrial applications that require high-purity water.
Fiberglass Media Filter: Uses corrosion-resistant and durable fiberglass as the main filter medium and is suitable for high-efficiency filtration and removal of tiny particles.
Ultrafiltration membrane filter: It uses microporous membrane filtration and is suitable for removing microorganisms, bacteria, viruses, etc. It is commonly used in drinking water and water treatment.
Sand and gravel mixed bed filter: This is a dual media filter with two layers (sand and gravel). These multimedia filters can filter out larger particles in the water, such as sediment and silt, and are commonly used in drinking water treatment plants.
Anthracite, sand and garnet multimedia filter: This is a multimedia filter with three layers. It can remove large and small particles from the water body, reduce the amount of sedimentation and turbidity of the water body, and is suitable for power plants.
Sand, anthracite and activated carbon multimedia filter: This is a multimedia filter with three layers, which uses a mixture of different types of filter media to provide multi-level filtering effects. It can effectively remove sediment and organic matter from the water. In addition, it can reduce odor by removing chlorine. It is mainly used in the manufacturing industry.
Zeolite multimedia filter: These are multimedia filters composed of zeolite and other layers. They are used where ion exchange and removal of ammonia and heavy metals are required.
10. Conclusion
Did you know? According to the World Health Organization, even in 2023, more than 2.2 billion people will still use poorly managed water services, which leads to a large number of waterborne diseases. This is where multimedia filters can help! If you are looking for quality water filtration system services, Fupeng Environmental Protection (FupengWater) is a good choice in the market.
FupengWater provides a variety of solutions such as carbon sand filters, quartz sand filters, multimedia sedimentation filters, multimedia sand filters, multimedia filter tanks, industrial multimedia filters, etc. to meet your commercial and industrial needs. Please contact FupengWater engineers to consult and customize multimedia filters that meet your water quality requirements.