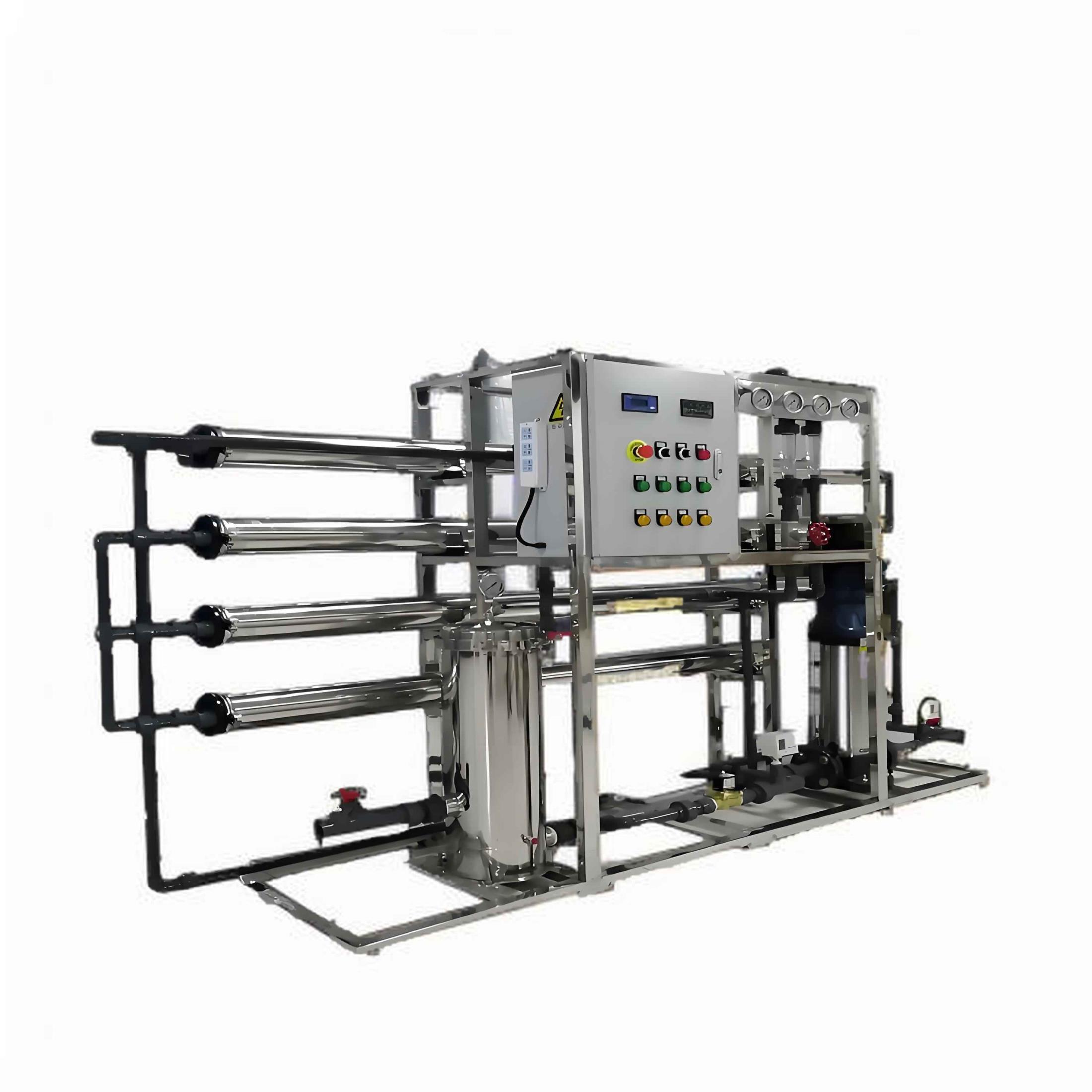
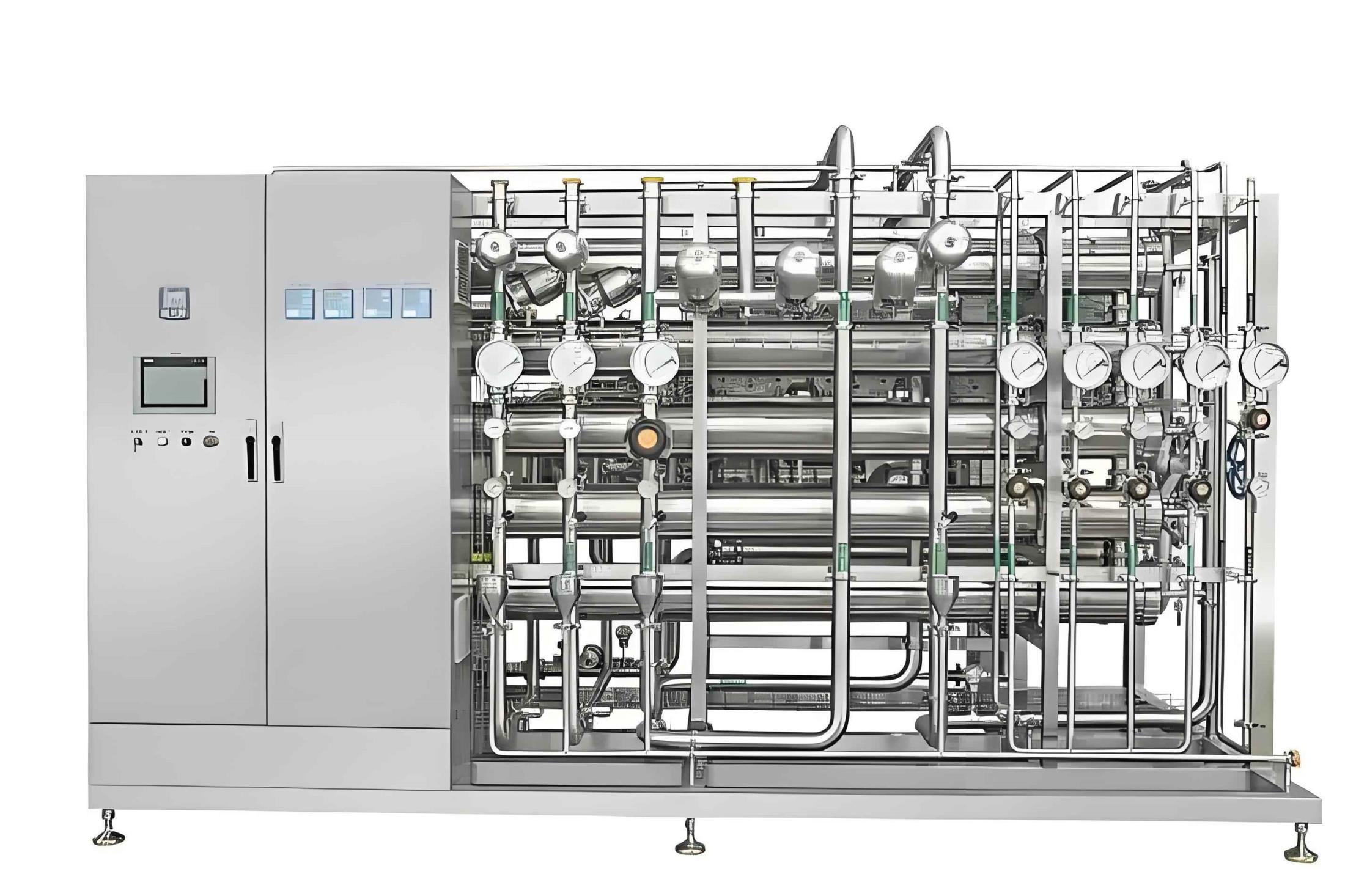
Nanofiltration NF SystemThe basic principle of nanofiltration membrane technology is to use pressure to separate soluble ions from water through a semipermeable membrane. Unlike dead-end filters, nanofiltration membranes utilize different hydraulic pr…
The basic principle of nanofiltration membrane technology is to use pressure to separate soluble ions from water through a semipermeable membrane. Unlike dead-end filters, nanofiltration membranes utilize different hydraulic properties, also known as cross-flow filtration.
Most nanofiltration membranes are composite materials supported by a polymer matrix and adopt a spiral design, rather than a flat or tubular structure. Currently, the predominant model in industrial applications is the spiral structure. To gain a deeper understanding of nanofiltration systems, you need to know the following information.
Similar to reverse osmosis (RO), nanofiltration systems recycle a certain percentage of the feed water, which differs from ultrafiltration (UF). Most nanofiltration membranes utilize a spiral wound structure.
FupengWater is a leading global supplier of industrial and commercial nanofiltration systems with over 20 years of experience specializing in removing impurities from water. Our nanofiltration systems ensure clean drinking water for a wide range of applications in the water treatment industry. View our range of nanofiltration systems for commercial sites and industrial plants to meet your water treatment needs.
In the water treatment industry, nanofiltration (NF) serves as a bridge between ultrafiltration (UF) and reverse osmosis (RO) membranes. It is sometimes referred to as loose or low-rejection RO membranes. Because NF membrane pore sizes range from 0.01 to slightly less than 0.001, it can also be referred to as tight ultrafiltration (UF). Generally speaking, NF membrane systems allow more salt to pass than RO membranes. Furthermore, NF membrane elements can produce the same water output as RO systems at 50% to 70% of the applied pressure.
In some applications, a 75% salt rejection is more advantageous than a 95% to 99% rejection, especially when using half the energy. Unlike reverse osmosis (RO) membrane elements, the performance of NF membrane elements offered by various membrane manufacturers varies significantly. For reverse osmosis (RO) membrane elements, any model with a sodium chloride rejection rate below 99.5%, especially for seawater, is considered inferior. However, for nanofiltration (NF) membrane elements, any model with a sodium chloride rejection rate of 40% or higher is considered suitable. NF membranes are also called "softening" membranes because, while their salt rejection rates may be 80% or lower, their hardness rejection rates are often well above 90%.
Heavy metal removal from wastewater
Pesticide removal from groundwater
Laundry wastewater recycling
Water softening
Nitrate removal
Nanofiltration membranes are used to filter low-total dissolved solids (TDS) water, removing organic matter and softening the water. Nanofiltration technology is used in numerous water and wastewater treatment industries, effectively removing ions and organic matter. Nanofiltration technology is also often used as a pretreatment for reverse osmosis (RO). In addition to water purification, nanofiltration membranes are also used in food, beverage, and pharmaceutical production.
While nanofiltration and reverse osmosis systems are similar in design and operational purpose, there are some significant differences between the two. The main difference is that nanofiltration is less rigorous than reverse osmosis. Nanofiltration operates at lower feed water pressures and cannot effectively remove singly charged ions from water like reverse osmosis membranes.
While reverse osmosis systems can remove up to 99% of chloride and sodium, nanofiltration membranes typically only remove 50% to 80%. This percentage depends on the membrane material type and manufacturing process. However, because nanofiltration effectively removes multiply charged ions, it is a preferred method for removing hardness from water without compromising total dissolved solids (TDS) as reverse osmosis does.
| Applications | Permeate | Concentration | Benefits of NF |
|---|---|---|---|
| Whey/Whey Permeate | Brackish Wastewater | Desalted Whey Concentrate | Allows for lactose and whey protein concentrate recovery and salt reduction |
| Textiles | Dyes | Water, Salt, BOD, COD, and Color | NF is used to desalinate dyes, resulting in higher-value products |
| Alkaline Cleaning Solutions | Alkaline Cleaning Solutions | BOD, COD, Suspended Solids, Alkaline Cleaners | Allows for recovery of alkaline cleaning solutions, reducing cleaning chemical costs |
| Acidic Solution Recycling | Acidic Solutions | BOD, COD, Calcium, Suspended Solids, Acidic Water | Allows for recovery of acidic solutions, reducing cleaning chemical costs |
| Water | Softened Water | Hard Water | Drinking Water Production Softened water reduces scaling of equipment and heat exchange surfaces |
| Antibiotics | Salty Waste | Desalination and Concentration of Antibiotics | NF Production of High-Value Pharmaceutical Products |
FupengWater's nanofiltration is a membrane filtration process most commonly used for low-total dissolved solids water, such as surface water and fresh groundwater, to soften water (remove multivalent cations) and remove disinfection byproduct precursors, such as natural and synthetic organic matter. Nanofiltration is also increasingly used in food processing applications, such as dairy, for simultaneous concentration and partial (monovalent ion) desalination.
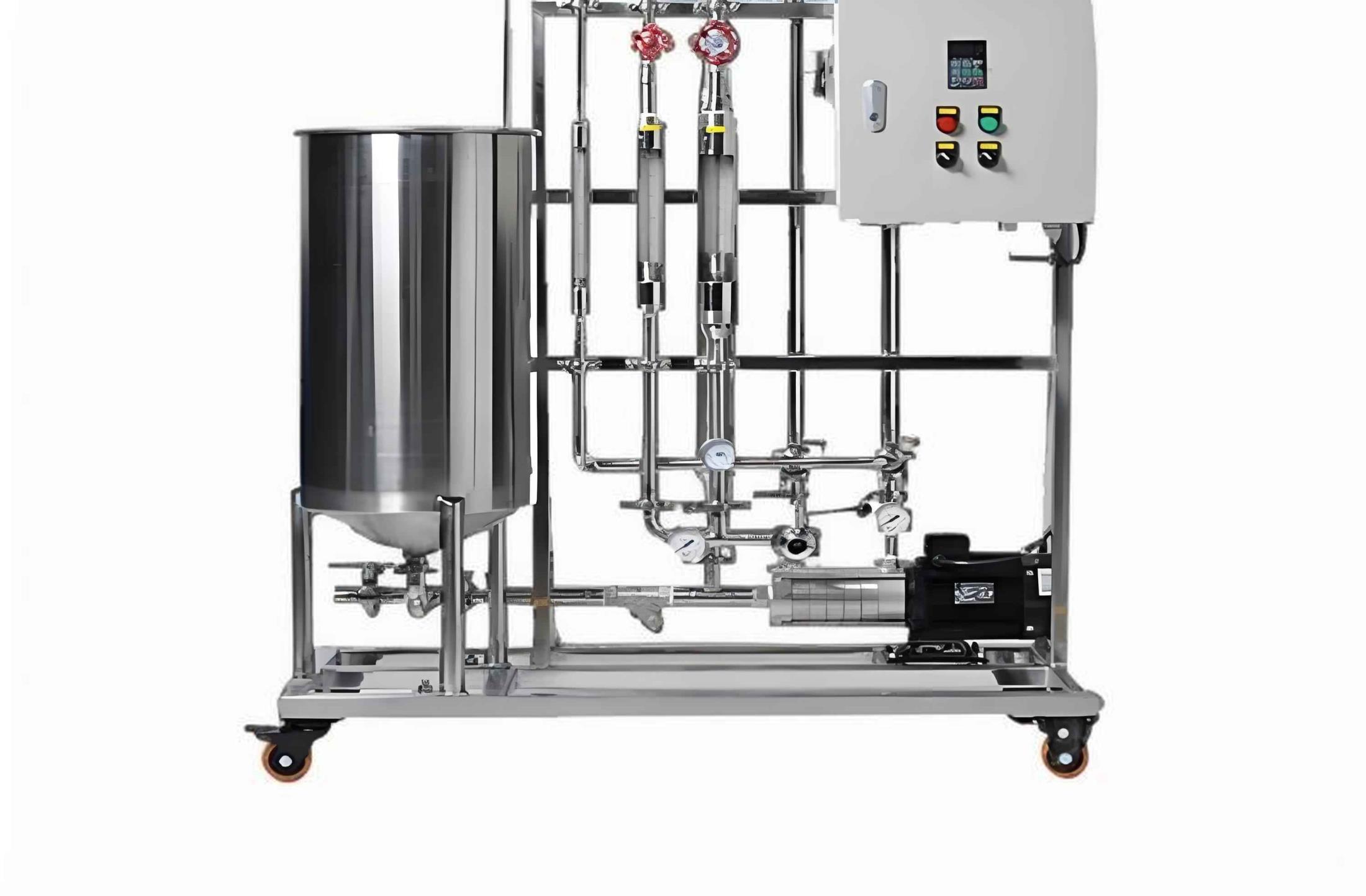
FupengWater offers a full range of standard and fully customizable nanofiltration systems, all designed using advanced 3D computer modeling and process design software to provide precise and customized solutions.
Maximum Inlet Water Temperature: 42°C
Inlet Water Pressure: 20 to 50 psi
Operating Pressure: 80 to 125 psi
H₂S Must Be Removed
Turbidity Must Be Removed
Maximum Iron Content: 0.05 ppm
Feed Water TDS: 0 to 1,000 ppm
Upgrading Equipment for Higher TDS
Anti-scaling Agent Required for Hardness Above 1 GPG
pH Tolerance: 3 to 11
Maximum Silica Tolerance: 60 ppm @ 60% Recovery
Operating at Higher TDS by Reducing Recovery
Powder-coated Carbon Steel Frame
8-inch TFC Spiral Wound Membrane
Stainless Steel Multistage Pump with TEFC Motor
Fiberglass Membrane Housing
5 Micron Cartridge Pre-Filter
460V/3ph/60Hz Power Requirements
Microprocessor-Based Control Panel
Programmable Time Delays and Setpoints
Status Indicator
Motor Starter
NEMA 12 Enclosure
Low-Pressure Switch
High-Pressure Switch
Filling Pressure Gauge
Permeate Conductivity Monitor
Permeate and Concentrate Flow Meters
Remote Monitoring/Control Options
Feed Water Conductivity Monitor
Membrane Cleaning Skid
Hourly Automatic Flush
Feed/Permeate Mixing
220V or 380-415V/3ph/50 or 60Hz
Product Tank Level Switch
Feed pH Controller with Sensor
Feed ORP Controller with Sensor
Flow Totalizer
Chemical Metering System
Media and Iron Pre-Filtration System
UV Sterilization System
Water Softener
Post-RO System
Containerized NF System
Nanofiltration is also increasingly common in food processing applications, such as textile wastewater treatment and dairy processing, for simultaneous concentration and partial (monovalent ion) desalination.



Copyright 2025 All Right Reserved. Hebei Fupeng Environmental Protection Technology Group Co., LTD