- 2025-10-13
What is a Reverse Osmosis System and How Does It Work?
Reverse osmosis is a highly efficient water treatment technology. It uses hydraulic pressure to force water through a semipermeable membrane, causing water molecules to permeate from a low-concentration salt solution to a high-concentration salt solution, reversing the natural flow of water. This process, commonly known as "reverse osmosis," simultaneously removes dissolved salts, impurities, and pollutants, further purifying the water.
We cover the following topics:
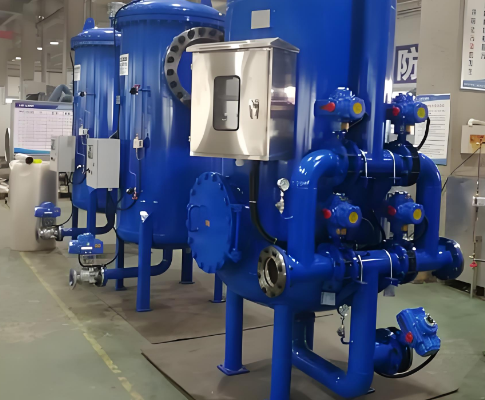
Reverse Osmosis (RO) Pretreatment
Reverse Osmosis (RO) Pretreatment Solutions
2. Scale Inhibitors/Descaling Equipment
Advantages of Reverse Osmosis:
Leading Technology: It is a high-tech separation technology that is safe, reliable, and widely applicable.
Energy Saving and Environmental Protection: It is a relatively energy-efficient and environmentally friendly technology with improved efficiency.High-Efficiency Filtration: It removes impurities, resulting in a purer solution. It can even filter out microorganisms such as viruses, organic matter, and bacteria.
Reverse Osmosis (RO) Pretreatment
It prevents scaling, contamination, and the need for frequent cleaning and premature failure of the RO membrane. Common problems with RO systems due to a lack of proper pretreatment include the following:
1.Reverse Osmosis Membrane Fouling
Membrane fouling occurs when large amounts of contaminants accumulate on the membrane surface and clog it. Municipal water supplies contain many contaminants that are invisible to the naked eye and pose no health risks. However, if the contaminants are present over a large enough area, they can quickly contaminate the RO system. Fouling is easily formed at the front end of a reverse osmosis system, causing a drop in system pressure, a subsequent decrease in water production, and a gradual increase in operating costs. This results in the need for membrane replacement or repeated cleaning. Therefore, proper pretreatment can minimize fouling issues.
Scaling can be caused by the following:
Filter media upstream of the RO unit
Sticks or particulates
Microorganisms
Microorganisms are one of the most common fouling issues. Because reverse osmosis membranes cannot tolerate disinfectants like chlorine, microorganisms can grow and multiply on the membrane surface, leading to serious fouling.
Filter media upstream of the RO unit, such as GAC activated carbon beds and softener beds, can cause drain leaks. Without effective filtration, the RO system may become fouled.
Two common fouling prevention methods are multi-media filters and microfiltration. In certain cases, filter cartridges can be used for filtration.
2.Chemical Attack
Because thin-film composite membranes are not resistant to chlorine, oxidants corrode them, creating membrane pores that are irreparable. Chemically corroded reverse osmosis membranes can lead to a sharp increase in permeate flow and a decrease in salt rejection. Without medication to prevent microbial growth, microorganisms on the reverse osmosis membrane rapidly grow, eventually fouling the membrane.
3.Mechanical Damage
Reverse osmosis systems contain piping and control valves. Forced activation can cause mechanical damage to the membrane. Excessive backpressure in the reverse osmosis system can also damage the membrane.
Reverse Osmosis (RO) Pretreatment Solutions
RO system pretreatment solutions can reduce contamination, chemical attack, and mechanical damage.
1.Multimedia Filtration
filters are designed to remove both large and small particles from water. Using a layered filtration method, each layer contains gravel, garnet, and sand, effectively removing particles of varying sizes. Larger anthracite is placed at the top, while heavier but smaller garnet is placed at the bottom, effectively filtering out impurities.
Microfiltration membranes (MMF) can remove particles as small as 15 to 20 microns. Using a coagulant, MMF membranes induce fine particles to coalesce into larger particles large enough for filtration, thus removing particles as small as 5 to 10 microns.
Experts recommend using a multi-media filter to prevent premature fouling of the reverse osmosis membrane when the influent sludge density index (SDI) exceeds 3 or the turbidity exceeds 0.2 NTU.Microfiltration membranes are typically operated with dead-end flow. In effect, all drinking water entering the membrane passes through it. Regularly flush the installed filter cake to remove it from the membrane surface.
2. Scale inhibitors and descaling agents/equipment
Antiscalants and descaling agents are added to the feedwater prior to the reverse osmosis system to help reduce the chemical buildup that can cause scaling. They prevent minerals from forming hard, adherent scale on pipe surfaces, instead forming softer, less adherent crystals.
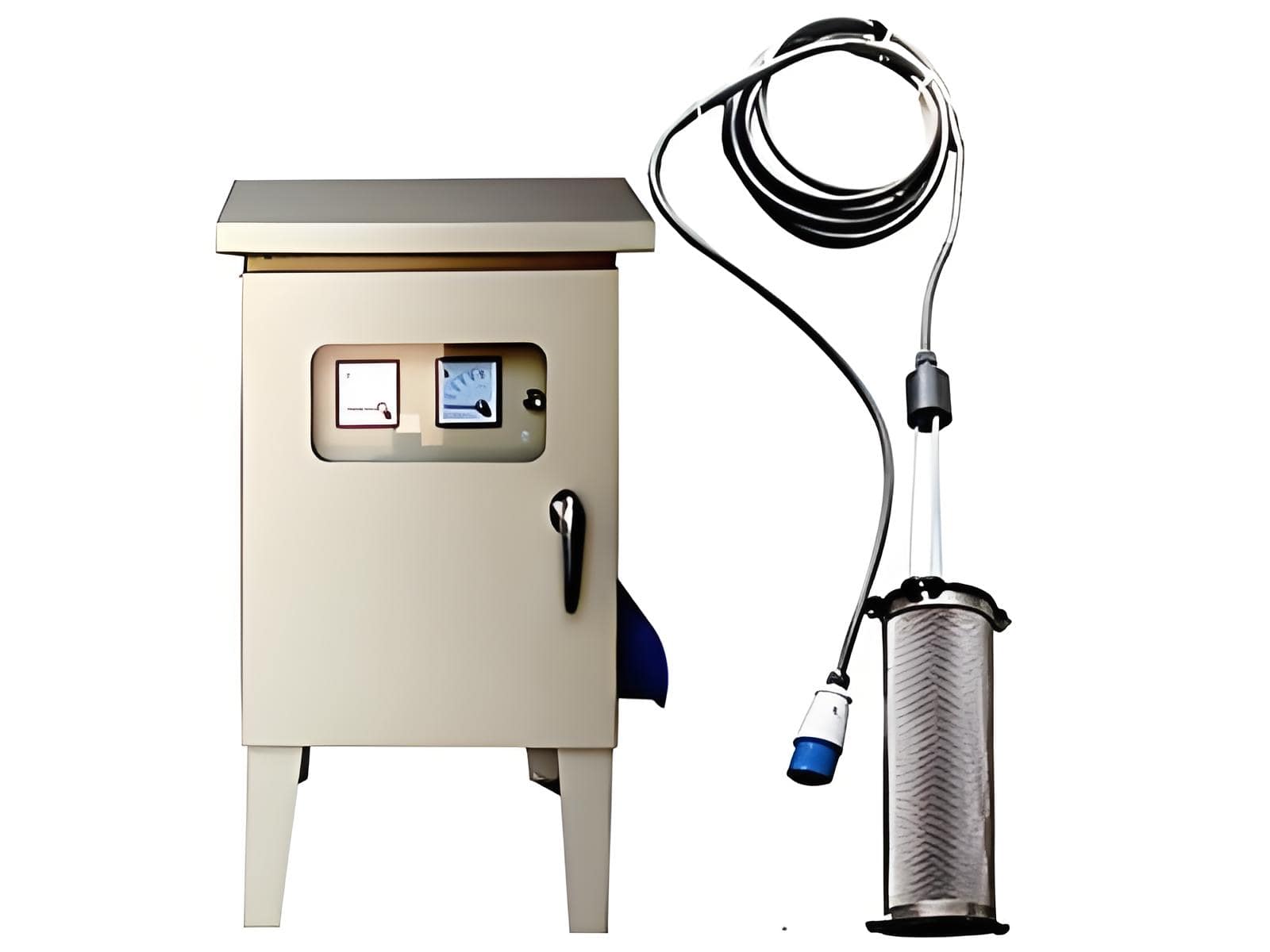

However, the selection and proper dosage of antiscaling agents and descaling agents should be considered based on the feedwater chemistry and reverse osmosis system design.
In conclusion
Reverse osmosis can reduce water contaminants and is a proven, safe, and effective technology.